Your breath doesn’t just smell bad—it’s trying to tell you something.
According to the International Association for Dental Research, approximately 25% of the global population suffers from chronic halitosis. But here’s what most people don’t realize: the specific type of smell your breath produces is often a direct indicator of what’s actually wrong.
Not all bad breath is created equal. A sulfur smell points to a completely different problem than a fruity odor. One might need simple oral hygiene changes, while another could signal a medical emergency.
This guide will help you decode what your breath is trying to tell you—and more importantly, what to do about it.
Why Different Smells Mean Different Problems
Your mouth, digestive system, and metabolic processes all produce distinct chemical compounds. When something goes wrong in any of these systems, specific volatile compounds escape through your breath.
These aren’t random odors. They’re biomarkers—measurable indicators of biological processes happening inside your body.
Dentists and physicians have long used breath odor as a diagnostic tool. In fact, a 2019 study published in the Journal of Breath Research found that trained medical professionals could identify certain diseases with up to 70% accuracy based solely on breath smell.
Let’s break down the seven most common breath odors and what each one reveals.

Diagnostic Index // Sector 7 Research
Morning Breath: 7 Warning Profiles
A clinical breakdown of scent profiles, biological triggers, and the required mechanical protocols for neutralization.
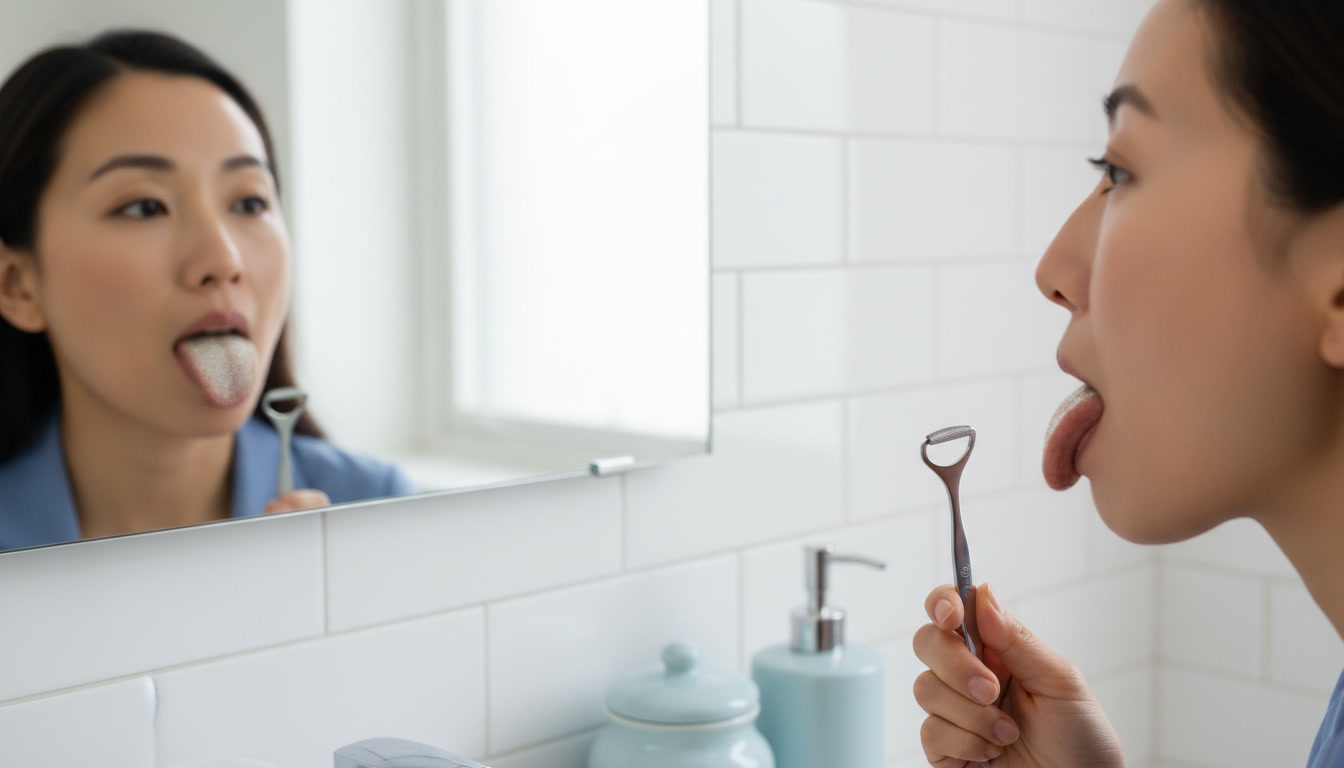
01. Sulfur / Rotten Egg Smell
The Mechanism: Anaerobic bacteria breaking down proteins on the tongue or in gum pockets, releasing volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) like hydrogen sulfide.
Clinical Context
University of Buffalo research confirms 90% of cases originate in the oral cavity. Common triggers include poor tongue hygiene, periodontitis, and tonsil stones.
PRO-TIP: Mechanical removal is the only fix. Tongue scraping removes up to 75% of VSC-producing bacteria per session.
02. Sour / Acidic Smell
The Mechanism: Acid Reflux (GERD). Stomach acid enters the oral cavity when the lower esophageal sphincter fails to seal correctly.
🚩 SEVERITY: MODERATE (Risk of esophageal damage)
03. Fruity / Sweet Smell
The Mechanism: Acetone/Ketone expulsion. This signals fat metabolism instead of glucose use.
• DIABETIC ALERT: Could indicate DKA (Life-threatening emergency). If sugar is >240 mg/dL, seek immediate care.
• DIETARY: Common in nutritional ketosis/fasting. Generally safe adaptation.
04. Fecal / Sewage Smell
The Mechanism: Severe sinus infection drainage or, in critical cases, a bowel obstruction. Infected mucus creates foul-smelling bacterial compounds.
05. Metallic Smell or Taste
The Mechanism: Iron from blood. CDC data shows nearly 50% of adults have periodontal disease, causing microscopic bleeding that smells metallic.
06. Fishy or Ammonia Smell
The Mechanism: Renal/Kidney dysfunction. When nitrogenous waste isn't filtered, it accumulates as urea and is expelled via breath.
⚠️ SEVERITY: HIGH (Requires medical renal screening)
07. Ammonia / Chemical Smell
The Mechanism: Excessive protein metabolism or severe dehydration. Without adequate water, the body cannot flush nitrogen-based waste products effectively.
The Bottom Line
Your breath smell isn’t just a social problem—it’s diagnostic information.
A sulfur smell usually means you need better oral hygiene. A fruity smell in a diabetic could save their life if caught early. A fishy smell might detect kidney disease before more serious symptoms appear.
Pay attention to what your body is telling you.
Most bad breath has a simple fix: better tongue cleaning, dietary changes, or treating an underlying infection. But some breath smells are your body’s early warning system for conditions that need medical attention.
Don’t ignore it. Don’t just mask it with mints.
Decode it. Address the root cause. And if you’re unsure, ask a professional.
Because sometimes, your breath is the only symptom you’ll get before something becomes serious.






